News
Study: Food insecurity risk related to diabetes later in life
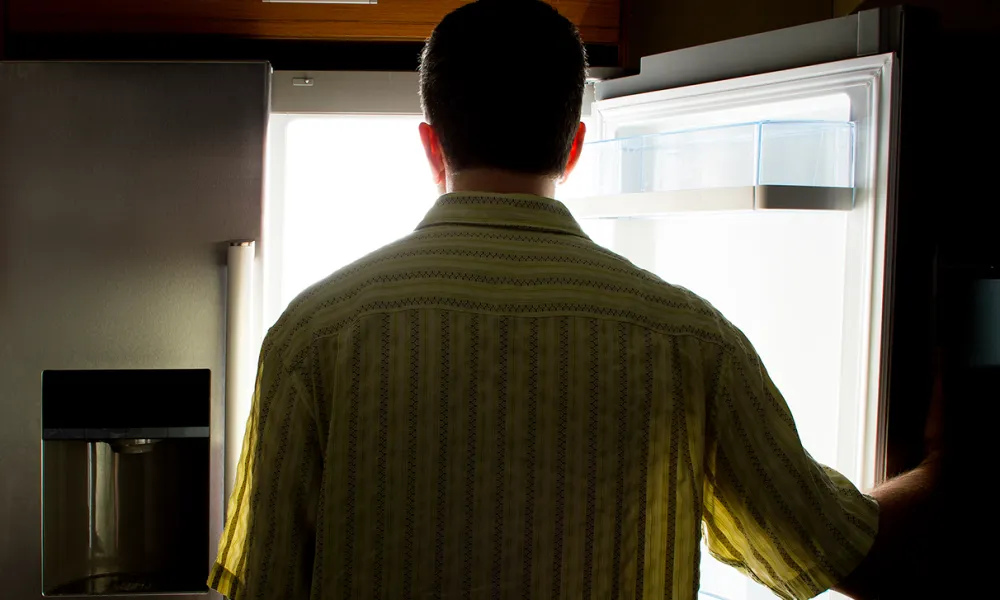

Young adults who were at risk of food insecurity had increased incidence of diabetes 10 years later, according to a Washington State University study.
In another study, published in the Journal of Nutrition, researchers analyzed data on nearly 4,000 people from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. They found that adults ages 24–32 who said they’d been worried about food running out in the last year showed greater incidence of diabetes, either through blood glucose tests or self-reports, at ages 32–42, compared to those who did not report food insecurity risk.
“When we look at the data 10 years later, we do see this separation in prevalence of diabetes: those that experienced risk of food insecurity at young adulthood are more likely to have diabetes in middle adulthood,” said Cassandra Nguyen, the study’s lead author and an assistant professor with WSU’s Institute for Research and Education to Advance Community Health or IREACH.
While the study could not identify the exact reason for this connection, previous research has shown that food-insecure households often have diets with lower nutritional values.
Nguyen added that people experiencing food insecurity can also get caught in a negative reinforcing cycle: when food insecurity is associated with a diet that contributes to disease risk, which then creates additional health care expenses, stressing a household’s economic resources and deepening food insecurity.
The study did not reveal differences among race or ethnicity, but the authors noted that the numbers of minorities in the sample may be too low to show a pattern.
For future work, the research team plans to investigate food insecurity risk and health issues within American Indian and Alaska Native populations. These communities are often left out of annual reports on food insecurity, which means they may be overlooked when reforms are made to food assistance programs and policies.
Nguyen recently led a review of 30 studies that found food insecurity estimates in Native populations varied widely, but even the lowest estimate far exceeds the prevalence among non-Hispanic white adults.
“It’s really important to ensure that individuals who are experiencing food insecurity are able to be identified and that they have resources made available to them to be able to break the cycle,” she said.
Terry A. Hurlbut has been a student of politics, philosophy, and science for more than 35 years. He is a graduate of Yale College and has served as a physician-level laboratory administrator in a 250-bed community hospital. He also is a serious student of the Bible, is conversant in its two primary original languages, and has followed the creation-science movement closely since 1993.
-
 Civilization3 days ago
Civilization3 days agoVirginia redistricting – the forgotten theater
-

 Civilization4 days ago
Civilization4 days agoWhat the Political Attacks on Fetterman Reveal
-

 Civilization5 days ago
Civilization5 days agoTrump’s SOTU Speech a Win, But It’s Not Enough
-
 Civilization5 days ago
Civilization5 days agoAt a Time of International Turmoil, ARC-ES Can Bring Energy Stability to the U.S.
-

 Clergy4 days ago
Clergy4 days agoDecapitating Amalek: Iran, Purim, and the Obligation to Act in Time
-

 Executive2 days ago
Executive2 days agoWaste of the Day: Rhode Island Overtime Payments Approach $300,000
-

 Civilization5 days ago
Civilization5 days agoTop Library Advocate: Backing Drag Queen Story Hour Supports Parental Choice
-

 Executive1 day ago
Executive1 day agoWaste of the Day: Prediction: Debt Will Soon Break Record


