News
NASA’s perseverance rover’s rock sample detecting most abundant organic molecules ever
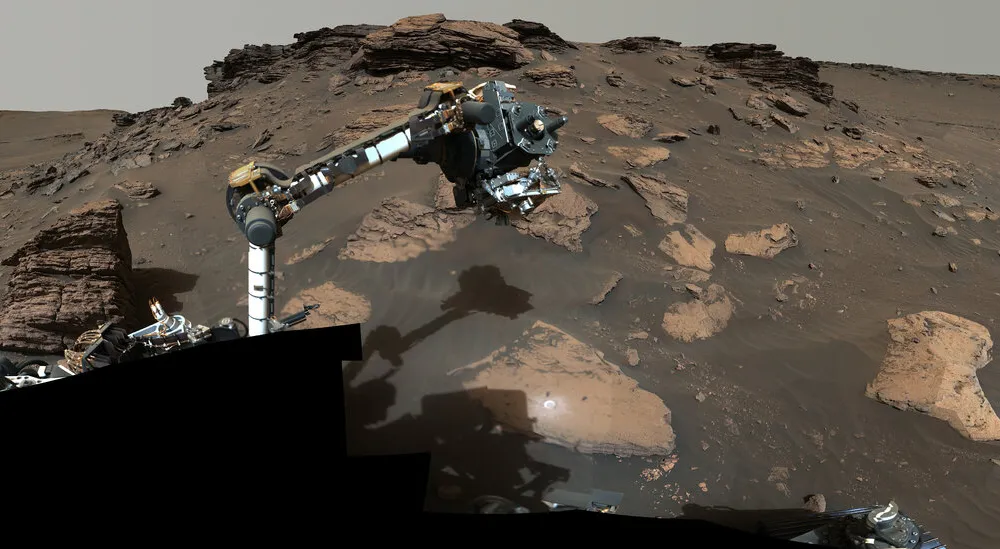

NASA’s Perseverance rover has obtained rock sample of Mars with the best ever traces of organic molecules.
While “organic” doesn’t necessarily mean life – as they can have geological origins – one thing is certain: the rover did it’s job.
An Organic molecule consists varied compounds, primarily made of Carbon along with Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur atoms. These are building block of many amino acids and carbohydrates which provides life.
In the second science campaign, the rover is collecting rock-core samples. The rover has collected a total 12 samples since July 7 from an ancient river delta in the Red Planet’s Jezero Crater.
“We picked the Jezero Crater for Perseverance to explore because we thought it had the best chance of providing scientifically excellent samples – and now we know we sent the rover to the right location. These first two science campaigns have yielded an amazing diversity of samples to bring back to Earth by the Mars Sample Return campaign,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA’s associate administrator for science in Washington.
45 Kilometer wide Jezero Crater is the host of a delta – an ancient fan-shaped feature that is estimated to be formed 3.5 billion years ago. Sedimentary rocks are under vigorous lookout by the rovers, as these rocks are formed when particles of various sizes settled in the once-wet environment.
During the first science campaign, the rover explored the crater’s floor examining the igneous rocks which were formed from deep inside the crust through magma, or during volcanic activities.
Project scientist Ken Farley said that along with diverse sedimentary rocks, the beautifully igneous rocks formed from crystallization were discovered. The rock, named “Wildcat Ridge”, is about 1 meter wide and was likely formed by mud and fine sand settlement by the evaporation of saltwater lake.
The Rover explored some of the surface of the rock and then analyzed it through an instrument called Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals, or SHERLOC.
The results indicated a class of organic molecule that are correlated with those of sulphate minerals, which can be used to yield significant information about the aqueous environment.
The geologic diversity of the samples already carried in the rover is so good that the rover team is looking into depositing select tubes near the base of the delta in about two months. After depositing the cache, the rover will continue its delta explorations.
Terry A. Hurlbut has been a student of politics, philosophy, and science for more than 35 years. He is a graduate of Yale College and has served as a physician-level laboratory administrator in a 250-bed community hospital. He also is a serious student of the Bible, is conversant in its two primary original languages, and has followed the creation-science movement closely since 1993.
-

 Civilization3 days ago
Civilization3 days agoA Better U.S. Strategy for Greenland Than Annexation
-

 Education3 days ago
Education3 days agoIgnoring the Science: The Curious Case of Cell Phone Bans
-

 Guest Columns5 days ago
Guest Columns5 days agoWaste of the Day: Thousands of Earmarks in Illinois State Budget
-

 Executive3 days ago
Executive3 days agoWaste of the Day: Utah University Trustees Don’t Know Their Job
-

 Education4 days ago
Education4 days agoA Solid Core Enlivens Free Speech and Viewpoint Diversity
-

 Civilization4 days ago
Civilization4 days agoEnd the Filibuster – Or Stop Pretending To Govern
-

 Executive4 days ago
Executive4 days agoWaste of the Day: $8 Water Filter Costs the Government $156
-
 Civilization2 days ago
Civilization2 days agoTrump’s Longest Speech, His Shortest Margin for Error


