News
Webb spots surprisingly massive galaxies in the early universe
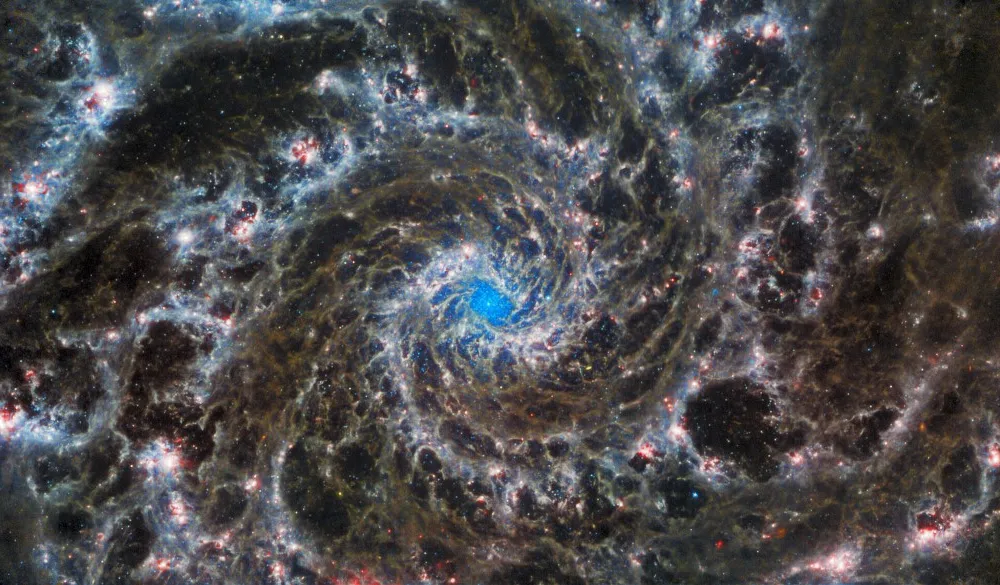

Six massive galaxies have been spotted by the James Webb Space Telescope, which is estimated to have emerged too soon after the Big Bang, according to a new study published in the journal Nature.
Being operational on its fullest fledge since last July, the JWST is having a ‘sneak peak’ deep into the Universe, at nearly 13 billion light-year distant sources of faint sparkles of light – which also suggests that it is looking back in time to the same extent. For its latest discovery, the telescope had surveillance on the galaxies from between 0.5 to 0.7 billion years after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago.
Webb’s NIRCam (Near Infrared Camera) instrument captured the invisible tint of light to our naked eyes, to observe six galaxies in a little-known region of the sky. Two of those galaxies were earlier noticed by the Hubble Space Telescope, but they were a lot fainter to catch sight of.
This discovery still needs to be confirmed by other measurements, as one of those is believed to have around 100 billion stars in its periphery, which is far more than expected by scientists, making it around the size of the Milky Way.
For this galaxy to achieve the same growth as that of our Milky Way in just 700 million years, it would have grown around 20 times faster, said Labbe, a researcher at Australia’s University of Technology. “According to the theory, galaxies grow from very small beginnings at early times, “ Labbe said, adding that such galaxies were expected to be between 10 to 100 times smaller.
This discovery can crack the previous model of the Big Bang, and highlight the unexpected pace of expanding the universe, allowing stars to form “much more efficiently”, as the early Universal stars are evaluated to have formed just 400 million years after the Big Bang. Labbe referred to the “black swan theory”, under which just one unexpected event can overturn our previous understanding—such as when Europeans saw the first black swans in Australia. He further termed the galaxies as “six black swans”, and added, “even if one of them turns out to be true, then we have to change our theories”.
Terry A. Hurlbut has been a student of politics, philosophy, and science for more than 35 years. He is a graduate of Yale College and has served as a physician-level laboratory administrator in a 250-bed community hospital. He also is a serious student of the Bible, is conversant in its two primary original languages, and has followed the creation-science movement closely since 1993.
-

 Executive4 days ago
Executive4 days agoSecret Service chief gets no solace
-

 Executive3 days ago
Executive3 days agoWaste of the Day: Louisville Taxpayers Pay Nearly $600,000 For Empty Building’s Maintenance, Security
-

 Guest Columns5 days ago
Guest Columns5 days agoFear Itself: Democrats’ Favorite Strategy Caused Their Current Chaos
-

 Executive3 days ago
Executive3 days agoWhere is Joe Biden – or Jill?
-

 Executive2 days ago
Executive2 days agoWaste of the Day: Throwback Thursday: Cities Used Crime Prevention Funds on Soccer Games, Paper Shredding
-

 Executive2 days ago
Executive2 days agoFacile and politically motivated suggestions
-

 Civilization5 days ago
Civilization5 days agoBuild Iron Dome in the United States To Prepare for Israel’s Worst Day
-
 Executive2 days ago
Executive2 days agoBiden makes farewell whisper


